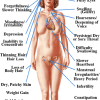
Autoimmune thyroid disease entails some sort of dysfunction from the body’s defense mechanism, in which the body does not distinguish its own organs and tissues, and rejects them, triggering inflammation and sometimes destruction. It can manifest either as hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). The main types of autoimmune thyroid disease are focal thyroiditis, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, atrophic thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Focal thyroiditis may not present with a goiter and blood examination will show normal or sub-clinical hypothyroidism. Sub-clinical hypothyroidism means that the thyroid stimulating hormone level is high which reflects an underactive thyroid but » » » [Read more]