Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland causes the state of a hyperactive thyroid known as hyperthyroidism and usually is associated by diffuse thyroid gland enlargement. One cause of hyperthyroidism is a condition known as Graves’ disease. It is often associated with enlargement of the eyes known as Graves’ ophthalmopathy and sometime associated with abnormality in the bone around the eyes, the orbit, known as Graves’ orbitopathy. It is believed that Graves’ disease is a result of an immunologic process.
Pregnancy has an important association with the development of Graves’ disease (hyperthyroidism). Some patients who were previously normal develop overactive thyroid gland during pregnancy because of the hormone changes that come with it.
Smoking may also complicate thyroid problems. It increases the chance of developing eye problems in patients with overactive thyroid gland.
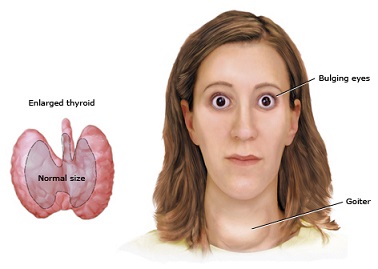
Photo taken from thenpmom.wordpress.com
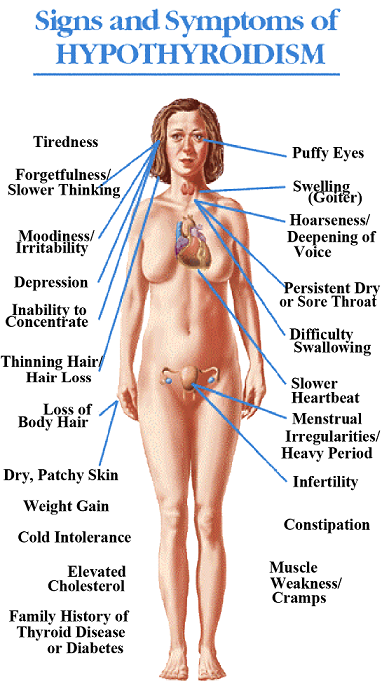
Overactive Thyroid Symptoms
Overactive thyroid or excessive levels of thyroid hormones may cause symptoms that include nervousness, fatigue, rapid heartbeat, difficulty in breathing, weight loss despite increased appetite, heat intolerance or increased perspiration, irregular menses specifically decreased menstrual cycles, diarrhea, enlarging eyes and enlarging thyroid gland perceived as an anterior neck mass.
The eye enlargement is said to be caused by spasm and retraction of the eyelids that lead to widening of the palpebral fissures so that the upper margin of the sclera (the white part of the eyes) is exposed. Early signs and symptoms of eye involvement due to overactive thyroid may include a sense of irritation resembling a foreign body sensation, excessive tearing which is worse on exposure to wind, and eye redness. Eye enlargement may be asymmetric and the patient sometimes complains of pressure behind the eyes. Blurring of vision and in severe cases color blindness may also be encountered but are not specific to hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone level).
Heart effects of overactive thyroids are due to the increased circulatory demands that result from hyper metabolism. Increased work of the heart may be sensed by palpitations described as feeling of rapid heartbeat. Rhythm irregularities may also occur such as atrial fibrillation.
The basal metabolic rate is increased that is why patients note weight loss despite increased appetite. This increase in metabolic rate is also manifested by heat intolerance described as feeling of hotness even in normal temperature or excessive sweating.
There can also be emotional liability with increased thyroid hormone levels. Nervousness can be attributed to rapid heartbeat or to the mood changes that can happen.
Patients with elevated thyroid hormones may also manifest with elevated liver enzymes and liver enlargement and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) may also occur with severe hyperthyroidism, but this should be worked up appropriately because it may be caused by a different disease. Frequency of bowel movement can also occur and is mistaken as a diarrhea in the acute setting. Prolonged hyper defecation may lead to malabsorption of fats and other nutrients.



 (3 votes, average: 3.33 out of 5)
(3 votes, average: 3.33 out of 5)