The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland located in the neck in front of the windpipe. The normal size is about 12-20grams with an abundant blood supply. The thyroid gland produces two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) which is consistently regulated by negative feedback to the brain specifically by thyroid stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary and thyrotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus. Excess or deficiency of these hormones is the underlying problem in thyroid diseases.
Iodine is a critical component in the production of thyroid hormones by the body. The thyroid gland obtains iodine from the blood. The blood iodine content, which is a reflection of iodine sufficiency in the diet, is very important in the normal production of the thyroid hormones which when deranged from normal levels is the basis of thyroid diseases.
Thyroid hormones have profound effects on nearly all organs of the body. Thyroid hormone is essential in the proper growth and development of the fetus during pregnancy and in children during their growth and development. More so, these hormones exert widespread influences on multiple aspects of metabolism in adults.
Thyroid hormones exert multiple effects on the liver and influences many processes in the body including metabolism of nutrients and energy production. Thyroid hormones can increase the metabolism of stored fat and protects against free radicals.
Thyroid hormones also affect the heart. Abnormal thyroid hormones are associated with heart problems that include increased or decreased heart rate, rhythm irregularities and heart failure.
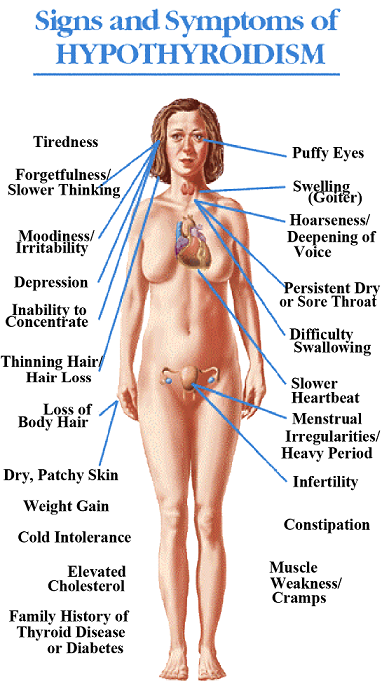
Symptoms that may suggest Thyroid Problems
Symptoms include palpitations, unexplained weight loss or weight gain, apathy, body weakness, heat or cold intolerance, changes in bowel movement and more. These symptoms depend on the abnormality of the thyroid hormone levels.
Some of the Types of Thyroid Problems
Overactive Thyroid
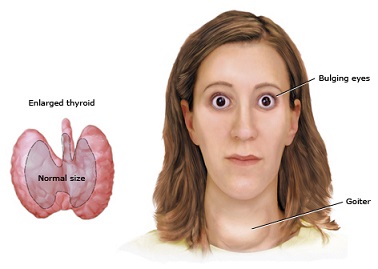
It is also known as hyperthyroidism where the thyroid glands produce excessive thyroid hormones. It is usually associated by diffuse thyroid gland enlargement.
Underactive Thyroid
It is also known as hypothyroidism. It is the condition of having an underactive thyroid. This is a state of thyroid hormone deficiency or lack of thyroid hormones.
Thyroid Cancer
They are the most common endocrine cancers. They can be classified whether they are benign or malignant.
Autoimmune Thyroid
It entails some sort of dysfunction from the body’s defense mechanism, in which the body does not distinguish its own organs and tissues, and rejects them, triggering inflammation and sometimes destruction. It can manifest either as hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).


 (9 votes, average: 4.33 out of 5)
(9 votes, average: 4.33 out of 5)