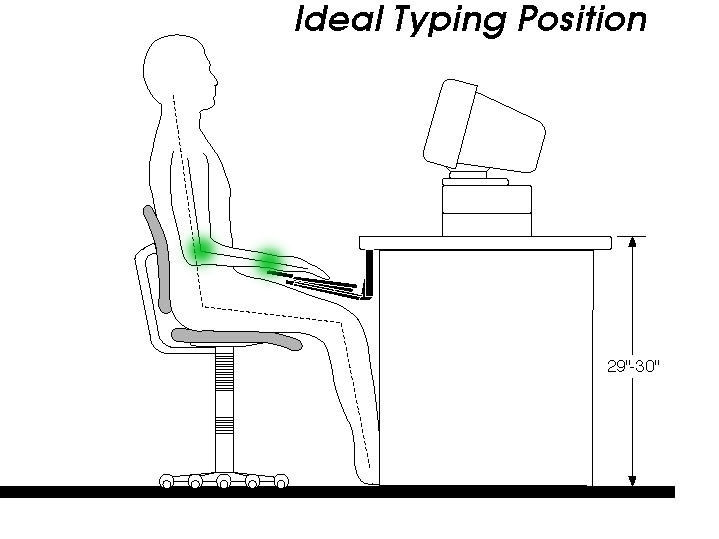
As most cases, repetitive stress injury is classified into two respective types. Below is the explanation of each type and how they differ from each other.
Type-1 Repetitive Stress Injury
Repetitive stress injury that fall in this category are based on one thing, it can be diagnosed by a physician through its recognized signs and symptoms. These symptoms usually involve inflammation and swelling of soft tissues like tendons or muscles affected by stress.
Some of the signs and symptoms that are clinically seen on an Repetitive Stress Injury case
Bursitis
Bursitis is defined as the inflammation of the bursa. Bursa means fluid-filled sac between a tendon and skin or a tendon and a bone that decreases friction between the tissues of the body. “itis” means inflammation or swelling. When something is inflamed, it tends to get painful, tender and there is a sensation of warmth around the affected area. Bursitis commonly occurs with cases of arthritis among middle age to old age persons.
Other inflammations that can be seen on Type-1 Repetitive Stress Injury
- Epicondylitis: inflammation of the area where bone and tendon join
- Rotator cuff syndrome: inflammation of muscles and tendons in the shoulder
- Tendonitis: inflammation of a tendon.
- Tenosynovitis: inflammation of the inner lining of the tendon sheath that contains the tendons which commonly occurs around the wrist, hand and forearm areas.
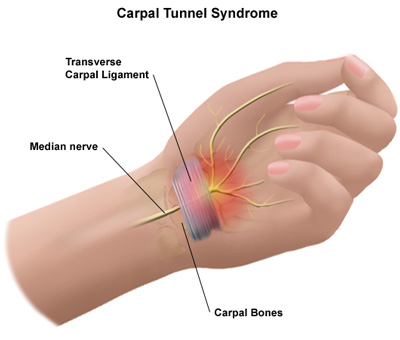
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Just like the rest of our body, our hand does have its respective nerve called the median nerve. This nerve supplies the sensation and movement to the palm side of the thumb and first three fingers except the smallest finger. The carpal tunnel is a small passageway of ligament and bones at the base of the hand which houses the median nerve and tendons.
Carpal tunnel syndrome happens when the median nerve becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. It is commonly seen on people whose jobs are those related to repetition of movements such as typing, sewing, painting, playing musical instruments and alike.
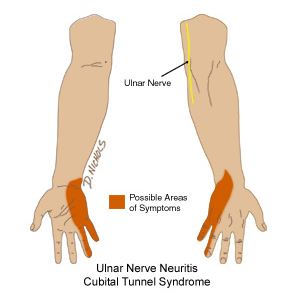
Cubital tunnel syndrome
Like the carpal tunnel, this concerns the compression of another nerve around the elbow area called the ulnar nerve. The ulnar nerve passes through the cubital tunnel which is found on the inner portion of the elbow called the medial epicondyle, the area is commonly termed to as the funny bone which makes the ulnar nerve susceptible to pressure. When it gets compressed the person experiences feeling of numbness and tingling mostly on the ring and little fingers.
Dupuytren’s contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is defined as the thickening, shrinking or tightening tissues beneath the skin on the palms of the hands and fingers. There is a development of small, painless nodule or lump in the tissue below the skin on the palm side of the hand which thickens over time making it hard or in severe cases, impossible to straighten or extend the fingers.
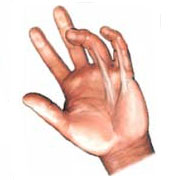
Picture of a Dupuytren’s contracture
Reynaud’s phenomenon
This commonly occurs during changes in temperature such as when its too cold nor too hot or during extreme emotions. It results in discoloration of the skin due to spasm or hardening of blood vessels decreasing the ability of blood to flow normally thus decreasing the supply of oxygen especially to the nose, toes, fingers and ears leading to numbness and development of carpal tunnel syndrome.
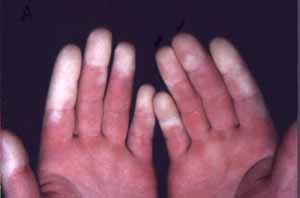
Picture of a Reynaud’s phenomenon
Writers’ cramp or hand dystonia
Writer’s cramp or “Scrivener’s Palsy” (19th century) usually happens during fine hand motor activities using the hand. It involves involuntary contractions of the muscles of the hands or other body parts known as dystonia. It happens when there is a repeated muscle strain using the hand and fingers during writing, painting, playing musical instruments and alike activities.

Picture of a writer’s cramp
Type-2 Repetitive Stress Injury
It is referred to as a non-specific pain syndrome for there are no obvious symptoms of the disease rather than a feeling of pain. This condition is different from Type-1 RSI because doctors are unable to identify it as an repetitive stress injury due to lack of clinical symptoms and manifestations like the ones explained above.



 (5 votes, average: 3.80 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 3.80 out of 5)