A thyroid tumor can be classified whether it is benign or malignant. Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine cancer. The management of these cancers involves surgery to remove the tumor with or without radioactive iodine to ablate remaining cancerous cells followed by medical therapy that usually consists of thyroid hormone replacement.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
95% of thyroid cancers belong to the well-differentiated type, the rest are medullary and anaplastic cancers. Well differentiated thyroid cancers can be further subdivided into Papillary thyroid cancer and Follicular thyroid cancer. The most common type of thyroid cancer is Papillary Thyroid Cancer.
Papillary thyroid cancer can occur at any age but most patients are between 30 and 50 years old. Women are affected more frequently than men. Most tumors are around 1-4 cm in size. A small percentage of the populations of papillary thyroid cancer patients have distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Once with distant metastasis, these patients are considered stage IV. After surgery, tumor recurrence may occur hence regular surveillance is necessary. Among these patients, 15% experience relapse and may indicate poor prognosis. Factors that may indicate poor outcome include increasing age at presentation, large tumor size, presence of locan invasion or distant metastasis.
Follicular thyroid cancer is usually seen in older people with an average age of diagnosis of 50 years old. 5-20% of patients with this type of thyroid cancer have distant metastasis at diagnosis. Metastasis is usually found in the lung or bone. Factors that may indicate poor outcome are similar in papillary thyroid cancer which includes increasing age at presentation, large tumor size, presence of locan invasion or distant metastasis.
Thyroid Cancer Symptoms
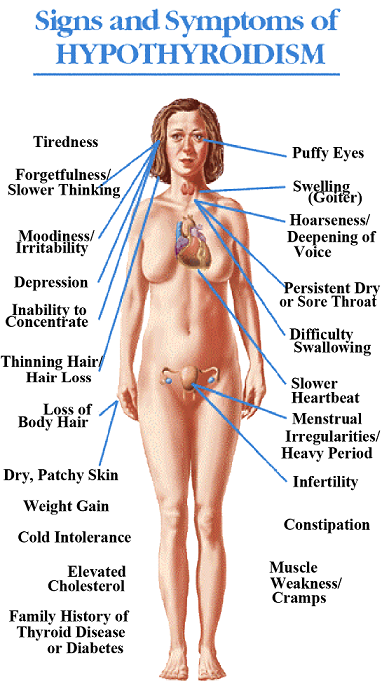
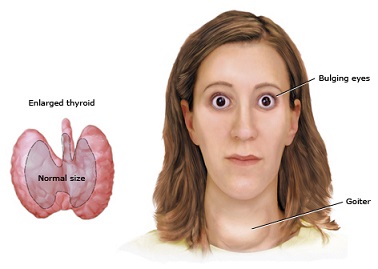
Signs and symptoms of thyroid cancer may include hoarseness, sudden increase in the size of the mass, sudden pain, difficulty in swallowing, difficulty in breathing, unexplained weight loss, bone pain and other non-constitutional symptoms.
Hoarseness is most commonly due to nerve involvement of the growing tumor. Sudden pain may also be due to nerve involvement but may also be due to tumor bleed. Difficulty of breathing and difficulty in swallowing are compressive symptoms that may be attributed to mass effect on the trachea or the esophagus, respectively. Unexplained weight loss is one of the most common sign of malignancies in general. Bone Pain on the other hand may already indicate poor outcome as it means involvement of the bones due to metastasis.


 (5 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)