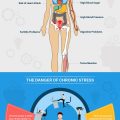
Stress had never been considered as detrimental as it is today. In the early days, it was stress that invoked a ‘fight or flight’ response and kept our ancestors safe from wild dangers. Now, the same stress is posing a risk of harm to the human body. It has been recognized as the No. 1 proxy killer disease by the esteemed American Medical Association. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have addressed the perils of workplace stress in the American Industry that claims an estimated $300 billion annually.

Source: https://www.glamour.com/story/stress-alone-can-cause-weight-gain
Effect of Stress on our Body
1. Physical Effects of Stress:
Nearly 40% of all adults owe their adverse health hazards to high levels of stress.
- Stress leads to high blood pressure levels that damage the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Stress kicks in the functioning of the hypothalamus in the brain, which directs the adrenal gland to increase the production of stress hormones. This causes over-activity in the blood vessels of the brain and can expose you to frequent headaches due to dilation of blood vessels and chemical activity in the brain.
- Long-term stress lowers your testosterone levels, causing a loss of sexual desire, erectile dysfunction in men, and irregular and heavier periods in women.
- People suffering from chronic stress not only find it difficult to stay shielded from illnesses such as flu, common cold, and cough but also take more time recover from such illnesses and injuries.
- It can also disturb your digestive health by subjecting you to acid reflux. Consequently, you are more likely to suffer stomach-aches, vomiting, nausea and other gastrointestinal problems.
- Stress adversely impacts a person’s cardiovascular health which in turn increases the risk of heart diseases, hypertension, and diabetes type I and II.
- The respiratory system of the body is also affected, resulting in rapid breathing. In individuals suffering from problems like emphysema or asthma, breathing evenly can be a daunting task.
- Chronic stress is also associated with physical symptoms such as fatigue, obesity, arthritis, skin conditions, muscle strain, etc.
Source: https://chrisgliddon.com/how-to-reduce-stress-my-7-stress-busting-techniques-67d01424a694
2. Cognitive Effects of Stress:
- Stress implicates damage to the brain and gives way to a myriad of mental ailments such as anxiety, irritability for no apparent reason, an increase in extreme bipolar behavior, and cases of excessive paranoia, oversensitivity, and panic attacks if things get worse.
- Forgetfulness, pessimism, and disorganization are other characteristic symptoms of stress.
- Often, it can lead to either a lack of sleep (“Insomnia”) or a desire to sleep for long hours. The American Psychological Association recorded that an estimated 40% of adults were affected by insomnia due to stress. Survey findings also point to the risk of anxiety and depression in people who sleep for less than 8 hours a night.
3. Behavioural Effects of Stress:
- A person may experience irrational mood swings and exhibit nervous behavior.
- A lack of appetite or an increased desire to eat, frequent outbursts, falling into self-deprecating habits, drug/alcohol abuse, and social withdrawal are common observances.
- Stress patients find it that much difficult to overcome the implicated effects of stress and are more likely to face higher risks of adverse outcomes.
4. Emotional Effects of Stress:
Untreated and chronic stress reactions constitute more than 50% of the emotional disorders a person experiences for a prolonged term.
- It contributes to decreased levels of self-esteem, confidence, lack of motivation and focus. It leads to an imbalance in the release of stress-related hormones which can cause hair fall.
- Chronic stress also breaks you down psychologically, leading to depression.
- There is an elevated sense of dissatisfaction coupled with the aforementioned life-threatening risks that deteriorate the bodies’ ability to recover and renders the immune system weak.
How can you get rid of stress?
1. Relaxation Exercises: Solutions to stress include meditation that helps in calming your muscles and bringing peace to your body. A recent study displayed a decrease in chronic headaches in almost half the participants when they consciously indulged in avoiding negative thoughts or “catastrophizing”. Yoga and other relaxation exercises also strengthen the immune system.
2. Healthy Food Habits: Eating right and exercising every once in a while, cutting back on caffeine, improving sleeping habits, taking in the fresh air, tuning in to the needs of your body and making time for pleasurable activities can have a positive effect on your mind. Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and other addictions during this phase is recommended.
Source: https://talkroute.com/7-tips-for-reducing-stress-at-work/
4. Professional Help: Several findings illustrate an inability in the average human being to cope with the hazards of stress and achieve stress management goals. According to the American Psychological Association, 2012, out of 64% people who admitted the importance of having the stress managed, only 37% were able to control their stress level. Thus, if the problem persists, it is best to consult with a psychologist and other licensed professionals to help you manage stress. Therefore, it’s convenient to ask a doctor online or consult a practicing professional for guidance.


 (5 votes, average: 4.20 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 4.20 out of 5)