The Common Cold is a mild viral infection of the nose, throat, sinuses, and upper airways caused by several distinct families of viruses such as the Coronavirus and Rhinovirus. An average adult may expect to get a cold approximately 2 – 4 times a year, while children may expect to get colds 3 – 8 times a year. Most colds last for 4 – 5 days, and while no cure is available for the common cold, over-the-counter medications may help reduce or eliminate your cold symptoms. Symptoms Colds result from a viral inflammation of the upper respiratory tract (nose to » » » [Read more]
Are you on the look out for natural remedies for Thyroid Disease that is truly effective? If so, read further to look for simple and instant solution to your natural remedies for thyroid disorders.
Thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism is relatively rare in children. According to reports, the yearly incidence is 8 per 1 million children who are younger than 15 years old and 1 per 1 million in children younger than 4 years old. Among these patients, Graves’ Disease is the most common cause. It is noted that girls are affected five times more than boys. A family history of hyperthyroidism should be sought because many have a positive family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases. A clinical profile includes several month records of progressive symptoms, of which, the most common are often behavioral disturbances such » » » [Read more]
Autoimmune thyroid disease entails some sort of dysfunction from the body’s defense mechanism, in which the body does not distinguish its own organs and tissues, and rejects them, triggering inflammation and sometimes destruction. It can manifest either as hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). The main types of autoimmune thyroid disease are focal thyroiditis, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, atrophic thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Focal thyroiditis may not present with a goiter and blood examination will show normal or sub-clinical hypothyroidism. Sub-clinical hypothyroidism means that the thyroid stimulating hormone level is high which reflects an underactive thyroid but » » » [Read more]
A thyroid tumor can be classified whether it is benign or malignant. Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine cancer. The management of these cancers involves surgery to remove the tumor with or without radioactive iodine to ablate remaining cancerous cells followed by medical therapy that usually consists of thyroid hormone replacement. Types of Thyroid Cancer 95% of thyroid cancers belong to the well-differentiated type, the rest are medullary and anaplastic cancers. Well differentiated thyroid cancers can be further subdivided into Papillary thyroid cancer and Follicular thyroid cancer. The most common type of thyroid cancer is Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Papillary » » » [Read more]
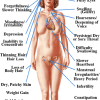
The condition of having an underactive thyroid is called hypothyroidism. This is a state of thyroid hormone deficiency or lack of thyroid hormones. It may be caused by an abnormality in the thyroid gland itself which is called primary hypothyroidism or by an insufficient level of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) causing under stimulation of the thyroid gland resulting to low thyroid hormone production. Underactive Thyroid Symptoms Signs and symptoms of thyroid hormone deficiency reflect the need for thyroid hormones in metabolism and its effect on all organs. Patients present with thickened features and puffy appearance. Swelling around the eyes and » » » [Read more]
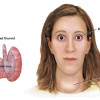
Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland causes the state of a hyperactive thyroid known as hyperthyroidism and usually is associated by diffuse thyroid gland enlargement. One cause of hyperthyroidism is a condition known as Graves’ disease. It is often associated with enlargement of the eyes known as Graves’ ophthalmopathy and sometime associated with abnormality in the bone around the eyes, the orbit, known as Graves’ orbitopathy. It is believed that Graves’ disease is a result of an immunologic process. Pregnancy has an important association with the development of Graves’ disease (hyperthyroidism). Some patients who were previously normal » » » [Read more]
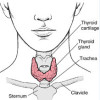
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland located in the neck in front of the windpipe. The normal size is about 12-20grams with an abundant blood supply. The thyroid gland produces two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) which is consistently regulated by negative feedback to the brain specifically by thyroid stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary and thyrotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus. Excess or deficiency of these hormones is the underlying problem in thyroid diseases. Iodine is a critical component in the production of thyroid hormones by the body. The thyroid gland obtains iodine from the blood. The blood » » » [Read more]
I specialize in adult diseases, diabetes, thyroid problems, thyroid biopsy (Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy), diseases of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands and other hormones as well as bone-related diseases such as osteoporosis and vitamin D deficiency.